MySQL’s Logical Architecture
MySQL’s most unusual and important feature is its storage-engine architecture, whose design separates query processing and other server tasks from data storage and retrieval
- MySQL has a layered architecture, with server-wide services and query execution on top and storage engines underneath.
- Although there are many different plugin APIs, the storage engine API is the most important.
- MySQL executes queries by handing rows back and forth across the storage engine API.
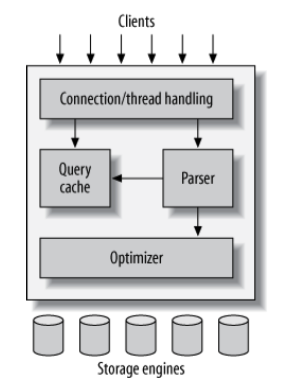
Parser
- MySQL parses queries to create an internal structure (the parse tree), and then applies a variety of optimizations.
- rewriting the query, determining the order in which it will read tables, choosing which indexes to use, and so on.
- You can pass hints to the optimizer through special keywords in the query, affecting its decision- making process.
Optimizer
- The optimizer does not really care what storage engine a particular table uses
- The optimizer asks the storage engine about some of its capabilities and the cost of certain operations, and for statistics on the table data.
- indexing and schema optimization
Query Cache
- store only SELECT statements, along with their result sets
Storage Engines
- The storage engine does affect how the server optimizes the query.
- The storage engines don’t parse SQL1 or communicate with each other; they simply respond to requests from the server.